Verbs are essential words in communication. Any verb is made up of two elements: a lexeme or root and a morpheme or ending. And this combination is what produces the different verb forms. The set of all verb forms is what makes up the verb conjugation. In other words, the verb conjugation consists of naming all its possible forms.
Verbs are essential words in communication. Any verb is made up of two elements: a lexeme or root and a morpheme or ending. And this combination is what produces the different verb forms. The set of all verb forms is what makes up the verb conjugation. In other words, the verb conjugation consists of naming all its possible forms.
Verbal structures
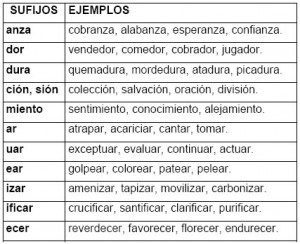
In the Spanish language all the verbs that exist belong to the first conjugation and are those that end in ar (to sing, swim or dance), to the second conjugation and are those that end in er (to return, know or have) and, for Finally, there are the verbs of the third conjugation, which are the ones that end in going (leaving, leaving or deciding).
As for the verb forms, these can be of two types: non-personal or personal forms. The first ones do not admit a personal reference pronoun (I, you, he, we, you and them) and are the infinitive form (ending in ar, er and ir), in gerund (verbs ending in ando, going or going ) and in participle (verbs that end in ado, ido and some cases of irregularity). In relation to personal forms, they are those that are accompanied by a personal pronoun (the three in the singular and the three in the plural already mentioned).
On the other hand, both personal and non-personal forms can be simple or compound, that is, a single verb form or a verb form accompanied by an auxiliary verb, specifically the verb haber. In other words, a simple verb form is made up of a single word and a compound one is made up of two words. The verb to have allows you to conjugate compound forms (you had played, they had run or they sung).
Verb conjugations and modes
 All verbs can be conjugated depending on the type of action of the verb, which can be indicative, subjunctive or imperative, which are the three modes in our language. This means that the same verb is conjugated in three different ways and each verb mode is made up of certain verb tenses.
All verbs can be conjugated depending on the type of action of the verb, which can be indicative, subjunctive or imperative, which are the three modes in our language. This means that the same verb is conjugated in three different ways and each verb mode is made up of certain verb tenses.
The indicative mood expresses real and concrete actions to describe reality (I sing, he jumps or we dance). The subjunctive mood is used for hypothetical or probable situations (either, we have or they decide). And verbs are conjugated in imperative mood when some kind of command or order is performed (for example, in sentences do your homework or go there right now).
Photos: iStock - Highwaystarz / JackF