When two or more things have a point of union there is a convergence, that is, a confluence, concurrence or concentration. The opposite implies a divergence or separation.
When two or more things have a point of union there is a convergence, that is, a confluence, concurrence or concentration. The opposite implies a divergence or separation.
Convergence of ideas and projects
If two people have similar approaches, they are converging, because there is a similarity between their positions.
In the context of a debate there is a logical discrepancy of opinions and views. Given this, it is possible that someone proposes a rapprochement of the positions and when this happens there is a convergence.
Let's imagine that two competing companies decide to merge for a specific project in order to obtain greater profitability. In this case, both entities will have to converge, which implies establishing joint strategies. Thus, the concept supposes a certain agreement or pact so that the initial differences are translated into coincidences.
In the field of biology
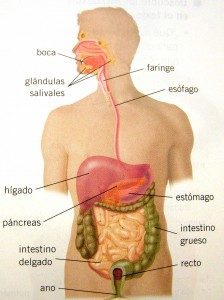
Within the framework of the theory of evolution, the so-called evolutionary convergence of species occurs. This happens when two different species adapt in the same way to a certain physical environment. The reverse process is known as evolutionary divergence.
 Convergent evolution between two species is not a spontaneous phenomenon but occurs gradually and slowly over many generations. In this sense, the laws of evolution are the engine of convergence as a strategy of adaptation to the environment. A clear example of this transformation is what has happened to aquatic animals, since all of them have developed fins to survive better. If we talk about evolutionary divergence, we could exemplify it with the functional differences between the wings of some species with respect to the legs of others.
Convergent evolution between two species is not a spontaneous phenomenon but occurs gradually and slowly over many generations. In this sense, the laws of evolution are the engine of convergence as a strategy of adaptation to the environment. A clear example of this transformation is what has happened to aquatic animals, since all of them have developed fins to survive better. If we talk about evolutionary divergence, we could exemplify it with the functional differences between the wings of some species with respect to the legs of others.
In the sphere of mathematics
It is called point convergence when a sequence of functions ends up converging at a point in another function. If this process is not punctual but stable, it is called uniform convergence.
In mathematical language there are convergence criteria. In this sense, there is a fairly intuitive general idea (for example, to add infinite things in order to get a number, those infinite things have to be smaller and closer to 0). Another convergence criterion is known as the Cauchy integral criterion, which is applied in the calculus of integrals.
Photos: iStock - PeopleImages / den-belitsky