 In the realm of physics, some chemical or physical processes absorb or emit heat. These processes are measurable and the area that is concerned with their measurement is calorimetry.
In the realm of physics, some chemical or physical processes absorb or emit heat. These processes are measurable and the area that is concerned with their measurement is calorimetry.
Key concepts
Temperature is a property and with it the thermal equilibrium between two different systems is determined. The flow of energy that is transferred between two systems is called heat. In other words, heat is the energy transferred between two systems or bodies that are at different temperatures. This flow always occurs from the higher temperature body to the lower temperature body.
Heat can be transferred in several ways: through radiation, conduction, or convection. In most real processes, all these phenomena are present to a greater or lesser extent.
The heat capacity of a body expresses the relationship between the amount of heat supplied and its corresponding increase in temperature. Different units can be used to express this parameter: joules to measure heat and degrees kelvin to measure temperature, in calories and degrees Celsius or in the British thermal unit (BTU) and degrees Fahrenheit.
On the other hand, the specific heat of a body expresses the relationship between the heat capacity of the material and the mass of that body. The units used to indicate specific heat are expressed in joules, kilograms, and degrees kelvin.
On the other hand, another system is also used: the amount of heat is expressed in calories, the mass in grams and the temperature in degrees centigrade.
If we take the specific heat of water as a reference, its formulation is as follows: 1 calorie / gram x degree centigrade.
The concept of sensible heat refers to the amount of heat added or removed that causes a change in temperature.
On the other hand, the concept of latent heat refers to the change of state that occurs in a body (for example, when water goes from a liquid to a gaseous state there is a change of state but not a change in temperature).
Practical applications of calorimetry
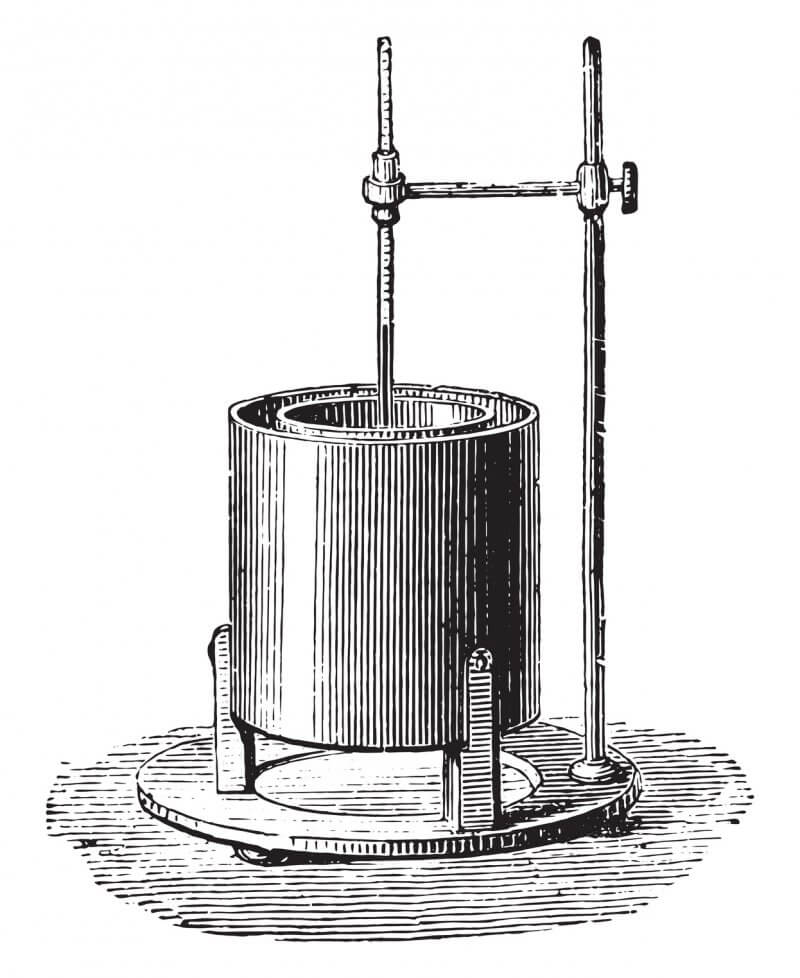
The calorimeter has a device to measure the temperature of a body, as well as a wall that prevents heat transfer in other directions. This device indicates the temperature in equilibrium between two substances with different temperatures.
The use of calorimeters is used, logically, for the measurement of calorific power in very different circumstances: in the food sector to assess the quality of a product, in thermodynamic studies of combustible waste or to know the energy balance in ecological studies.
Photo: Fotolia - Morphart