 In the field of epidemiology, the incidence term is undoubtedly one of the most important since it has to do with the increase that a disease or epidemic can show over time, thus allowing its analysis and possible solution.
In the field of epidemiology, the incidence term is undoubtedly one of the most important since it has to do with the increase that a disease or epidemic can show over time, thus allowing its analysis and possible solution.
It can be essentially defined as the number of new cases of disease that appear in a more or less specific situation in a given period of time. In this sense, the incidence is then a limited number of cases that appear and that, properly projected in graphs and analyzes, allow us to understand the growth of a disease or epidemiological condition in a limited time space.
The notion of incidence is related to that of risk since it always implies the possible projected growth of a disease according to the analysis of the new cases in which such a condition is present
In this way, incidence becomes one of the most important and useful values for epidemiologists since it not only allows us to look back and analyze the evolution of certain diseases in certain temporal-spatial conditions, but also allows us to project towards the future. a growth or decrease of the disease according to the values analyzed.
The incidence of a disease should not be confused with the prevalence
While the first is related to the notion of incident and, therefore, to that of something that is specific to a time and place, the second is related to the notion of permanence and that is why it means the total number of patients or cases of disease. in a population. Incidence, on the other hand, represents the number of new cases in a given period of time.
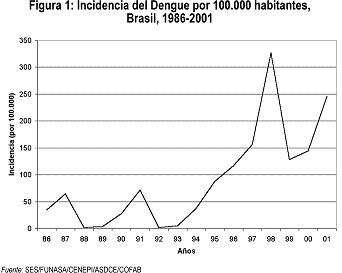
Examples for both cases would be, for incidence, dengue cases that appear in a population in a period of one year; for prevalence, the total dengue cases in a population since that disease has been discovered.